Types, Standards, and List of Coaxial Cables
What are coaxial cables? (Basic Structure, Uses and Features)
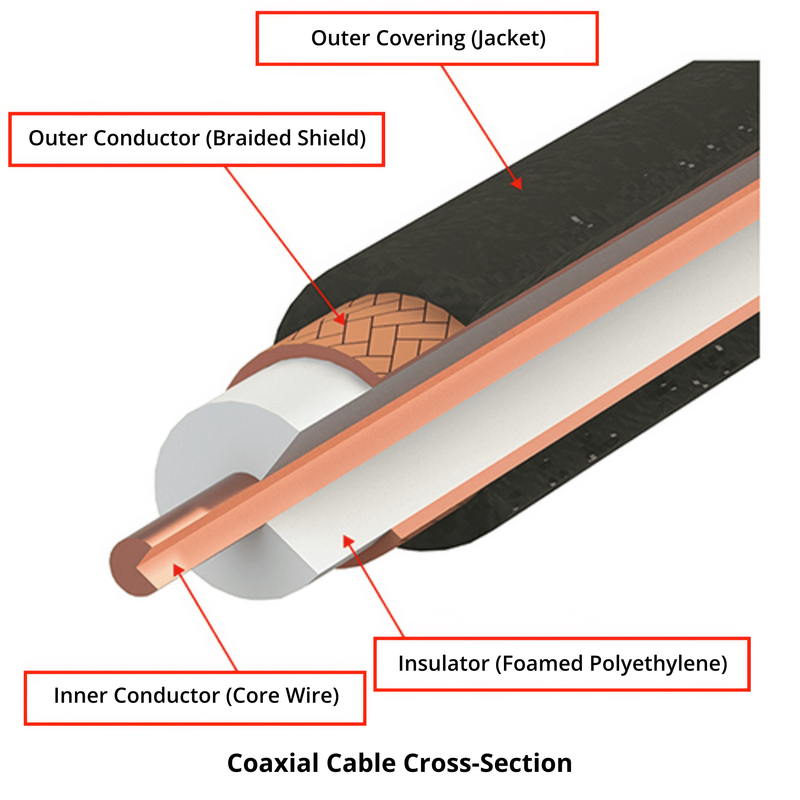
Coaxial cable is a type of covered wire used in telecommunications, also called RF cable. They are used to efficiently transmit radio frequency (RF) signals.
To transmit RF signals efficiently from the transmitter to the receiver, it is necessary to minimize loss and avoid reflections.
For this reason, coaxial cables are characterized by unbalanced connections, minimal leakage of electromagnetic waves to the outside, and a certain degree of flexibility.
Coaxial cables are often manufactured to MIL standards.
Standard and type of coaxial cable (RG (MIL standard))
U.S. Military Procurement Material Standard MIL standard cables start with “RG (Radio Guide)” and are also called mil-spec.
Example : RG-58A/U
RG : Radio Guide (abbreviation of Radio frequency coaxial cable General purpose, some say)
58 : Type number (assigned in the order of establishment, not in order of thickness as in the JIS standard)
A : Assignment code (Alphabetical order, such as A to C, with standard change symbols) * U: Universal (for general use)
U : Universal (for general use)
RG-58A/U has a single wire inner conductor (core wire), while RG-58A/U has a stranded inner conductor (stranded wire).
However, the difference caused by the assigned number varies from product to product.
How to select coaxial cables (points not to fail)
Generally, coaxial cables are selected in the following order.
In many cases, the connector category (type) is determined first, according to the transmitting device, receiving device, antenna, etc., and then the cable selection process begins.
Impedance
50Ω: Power transmission for radio equipment, etc., 75Ω: For video and audio signal transmission
Impedance selection is made in accordance with transmitting equipment, receiving equipment, antennas, etc.
Frequency Band
Different cables have different usable frequencies. The same is true for connectors.
At high frequencies above 18 GHz, special cables are used.
Cable Thickness
Depending on where you are wiring, cables that are too thick may not fit.
This is often not a concern for external wiring, but thin cables are needed for wiring inside equipment.
Total Cable Length
In general, the longer the overall cable length, the more loss will occur. For external wiring in particular, a thicker cable with less loss is selected.
Cable Stiffness
In general, the thicker the cable, the stiffer and less maneuverable it becomes. Depending on the usage environment, it is necessary to find a cable that is thin and easy to handle, paying attention to the bending radius.
Other
Selection should be made according to the operating environment, such as waterproof, high temperature, high humidity, etc.
Trivia: Bending Radius
Coaxial cable is flexible to a degree, but it must not be bent beyond its minimum bend radius. If the bend is too tight, signal transmission will be affected. This radius is often denoted as R (bending radius).
The minimum bend radius is typically 10x the cable’s outer diameter. Exceeding this limit can cause signal degradation or physical damage.
List of Coaxial Cables
This is a list of coaxial cables.
Impedance, construction, materials, and diameters are indicated. The values shown are typical and may vary depending on the cable manufacturer.
Abbreviations for construction and materials are explained below.
List
RG-5/U
Impedance: 52.5Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 1.295
Inner conductor(Configuration): AC
Insulator(Diameter): 4.7
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 6.3
Outer conductor(Configuration): AA
Outer sheath(Diameter): 8.4
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-8/U
Impedance: 52Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.724
Inner conductor(Configuration): AC
Insulator(Diameter): 7.2
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 8.1
Outer conductor(Configuration): A
Outer sheath(Diameter): 10.3
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-9/U
Impedance: 51Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.724
Inner conductor(Configuration): S
Insulator(Diameter): 7.1
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 8.7
Outer conductor(Configuration): SA
Outer sheath(Diameter): 10.7
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-10/U
Impedance: 52Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.724
Inner conductor(Configuration): AC
Insulator(Diameter): 7.2
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 8.1
Outer conductor(Configuration): A
Outer sheath(Diameter): 10.3
Outer sheath(Material): PVC*
* RG-10/U has an additional braided outer covering (finished O.D. 12.0 mm) over the outer sheath.
RG-11/U
Impedance: 75Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.404
Inner conductor(Configuration): T
Insulator(Diameter): 7.2
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 8.1
Outer conductor(Configuration): A
Outer sheath(Diameter): 10.3
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-14/U
Impedance: 52Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 2.591
Inner conductor(Configuration): AC
Insulator(Diameter): 9.4
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 11.2
Outer conductor(Configuration): AA
Outer sheath(Diameter): 13.8
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-17/U
Impedance: 52Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 4.775
Inner conductor(Configuration): AC
Insulator(Diameter): 17.3
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 18.6
Outer conductor(Configuration): A
Outer sheath(Diameter): 22.1
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-55/U
Impedance: 53.5Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 0.813
Inner conductor(Configuration): AC
Insulator(Diameter): 2.9
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 4.2
Outer conductor(Configuration): TT
Outer sheath(Diameter): 5
Outer sheath(Material): PE
RG-58/U
Impedance: 53.5Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 0.813
Inner conductor(Configuration): AC
Insulator(Diameter): 2.9
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 3.6
Outer conductor(Configuration): T
Outer sheath(Diameter): 5
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-58A/U
Impedance: 50Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 19 / 0.180
Inner conductor(Configuration): T
Insulator(Diameter): 2.9
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 3.6
Outer conductor(Configuration): T
Outer sheath(Diameter): 5
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-59/U
Impedance: 75Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 0.643
Inner conductor(Configuration): CW
Insulator(Diameter): 3.7
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 4.5
Outer conductor(Configuration): A
Outer sheath(Diameter): 6.2
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-62/U
Impedance: 93Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 0.643
Inner conductor(Configuration): CW
Insulator(Diameter): 3.7
Insulator(Material): SSt
Outer conductor(Diameter): 4.5
Outer conductor(Configuration): A
Outer sheath(Diameter): 6.2
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-62A/U
Impedance: 93Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 0.643
Inner conductor(Configuration): CW
Insulator(Diameter): 3.7
Insulator(Material): SSt
Outer conductor(Diameter): 4.5
Outer conductor(Configuration): A
Outer sheath(Diameter): 6.2
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-71/U
Impedance: 93Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 0.643
Inner conductor(Configuration): CW
Insulator(Diameter): 3.7
Insulator(Material): SSt
Outer conductor(Diameter): 5
Outer conductor(Configuration): TT
Outer sheath(Diameter): 5.8
Outer sheath(Material): PE
RG-142B/U
Impedance: 50Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 0.991
Inner conductor(Configuration): SCW
Insulator(Diameter): 2.9
Insulator(Material): TFE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 4.2
Outer conductor(Configuration): SS
Outer sheath(Diameter): 5.2
Outer sheath(Material): FEP
RG-174/U
Impedance: 50Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.160
Inner conductor(Configuration): CW
Insulator(Diameter): 1.5
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 2
Outer conductor(Configuration): T
Outer sheath(Diameter): 2.5
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-178B/U
Impedance: 50Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.102
Inner conductor(Configuration): SCW
Insulator(Diameter): 0.86
Insulator(Material): TFE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 1
Outer conductor(Configuration): S
Outer sheath(Diameter): 1.8
Outer sheath(Material): FEP
RG-187A/U
Impedance: 75Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.102
Inner conductor(Configuration): SCW
Insulator(Diameter): 1.5
Insulator(Material): TFE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 2
Outer conductor(Configuration): S
Outer sheath(Diameter): 2.7
Outer sheath(Material): TFE
RG-188A/U
Impedance: 50Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.170
Inner conductor(Configuration): SCW
Insulator(Diameter): 1.5
Insulator(Material): TFE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 2
Outer conductor(Configuration): S
Outer sheath(Diameter): 2.6
Outer sheath(Material): TFE
RG-196A/U
Impedance: 50Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.102
Inner conductor(Configuration): SCW
Insulator(Diameter): 0.86
Insulator(Material): TFE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 1.3
Outer conductor(Configuration): S
Outer sheath(Diameter): 2
Outer sheath(Material): TFE
RG-223/U
Impedance: 50Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 1 / 0.889
Inner conductor(Configuration): S
Insulator(Diameter): 2.9
Insulator(Material): PE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 4.2
Outer conductor(Configuration): SS
Outer sheath(Diameter): 5.3
Outer sheath(Material): PVC
RG-316/U
Impedance: 50Ω
Inner conductor(Number of strands/wire diameter): 7 / 0.170
Inner conductor(Configuration): SCW
Insulator(Diameter): 1.5
Insulator(Material): TFE
Outer conductor(Diameter): 2
Outer conductor(Configuration): S
Outer sheath(Diameter): 2.4
Outer sheath(Material): FEP
Coaxial cable Operating temperature range for each outer sheath
The operating temperature range of coaxial cables is mainly determined by the material of the outer sheath. *It may also be affected by the material of the insulation.
The operating temperature range for each material is as follows
List
PVC
Vinyl Chloride
-15~60℃
PE
Polyethylene
-40~75℃
TFE
Tetrafluorocarbon Resin (Teflon)
-70~250℃
FEP
4-6 Fluorinated Ethylene-propylene Copolymer
-70~200℃
Abbreviations for Coaxial Cable Construction and Materials
The names of construction types and materials, which were indicated by abbreviations in the aforementioned list of coaxial cables, are shown below.
Inner Conductor
AC
Copper alloy with traces of silver, lead, or tin
T
Tinned soft copper wire
S
Silver plated soft copper wire
CW
Copper-coated steel wire
SCW
Silver-plated copper-clad steel wire
Insulator
PE
Enhanced polyethylene
SST
Polyethylene cordel + polyethylene pipe
TFE
Tetrafluorocarbon resin (Teflon)
Outer conductor
A
Single-layer bare copper wire braid
AA
Double-layer bare copper wire braid
T
Single-layer tin-plated copper wire braid
TT
Double-layer tin-plated copper wire braid
S
Single-layer silver-plated copper wire braid
SS
Double-layer silver-plated copper wire braid
SA
Single-layer silver-plated copper wire braid + single-layer bare copper wire braid
Outer sheath
PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
PE
Polyethylene
TFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE / Teflon)
FEP
Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene copolymer (ETFE-HFP copolymer)
FAQs
QWhat types of coaxial cables are there?
QWhat types of coaxial cables are there?
Coaxial cables are mainly classified into the following two standards:
- JIS standard (for use in Japan): 5C-2V, 3D-2V, 5D-FB, etc.
- RG (MIL standard) (U.S. military standard): RG-58, RG-174, RG-316, etc.
It is important to select the appropriate standard according to the application.
QWhat types of impedance are there for coaxial cables?
QWhat types of impedance are there for coaxial cables?
Generally, there are two types: 50Ω and 75Ω. 50Ω is commonly used for radio communications and high-frequency circuits, while 75Ω is used for television broadcasting and video transmission.
QHow is the thickness of a coaxial cable determined?
QHow is the thickness of a coaxial cable determined?
The outer diameter (thickness) of a coaxial cable varies depending on its transmission performance and application.
- Thicker (RG-8, RG-14): For low loss and long distance transmission
- Standard (RG-58, RG-62): For general communications equipment
- Thinner (RG-174, RG-316): For tight spaces and high-frequency applications
For long-distance or high-frequency applications, it is ideal to select a thicker cable. In general, thicker cables have lower attenuation.
QHow can I order coaxial connectors, and what support do you offer?
QHow can I order coaxial connectors, and what support do you offer?
Ordering is simple—you can purchase our coaxial connectors directly on our website or contact our sales team for assistance. We also provide full technical support, including datasheets, CAD models, and application notes, to help you pick the perfect connector for your project.